Medical-grade adhesives are typically coated on a variety of backings to form medical fixation materials. When creating any medical-grade adhesive, careful consideration should be taken in the selection of the proper adhesive type, backing substrate and coating technique.
Medical-grade adhesives are typically coated on a variety of backings to form medical fixation materials. These advanced materials are widely used in many healthcare applications, but most are primarily designed to be used directly on the skin or to hold medical devices in place. Some of the applications include medical electrodes, advanced wound care dressings, ostomy devices, microplate sealing for diagnostic applications, surgical drapes, IV site dressings, diabetes care devices, pulse oximeters and many other point-of-care and wearable device applications.
When creating any medical-grade adhesive, careful consideration should be taken in the selection of the proper adhesive type, backing substrate and coating technique. Following are the requirements and considerations for some common applications.
Application-Specific Requirements
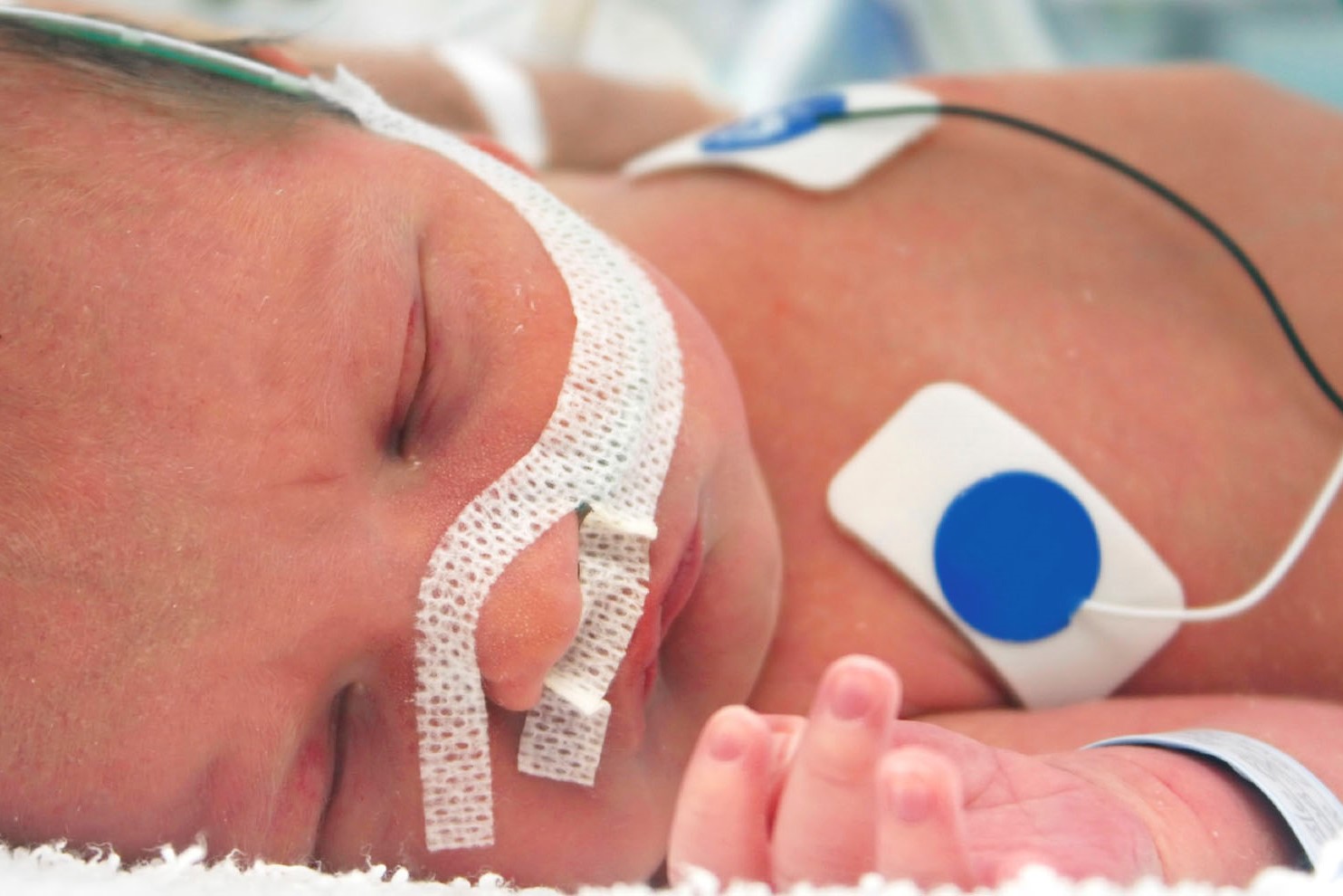
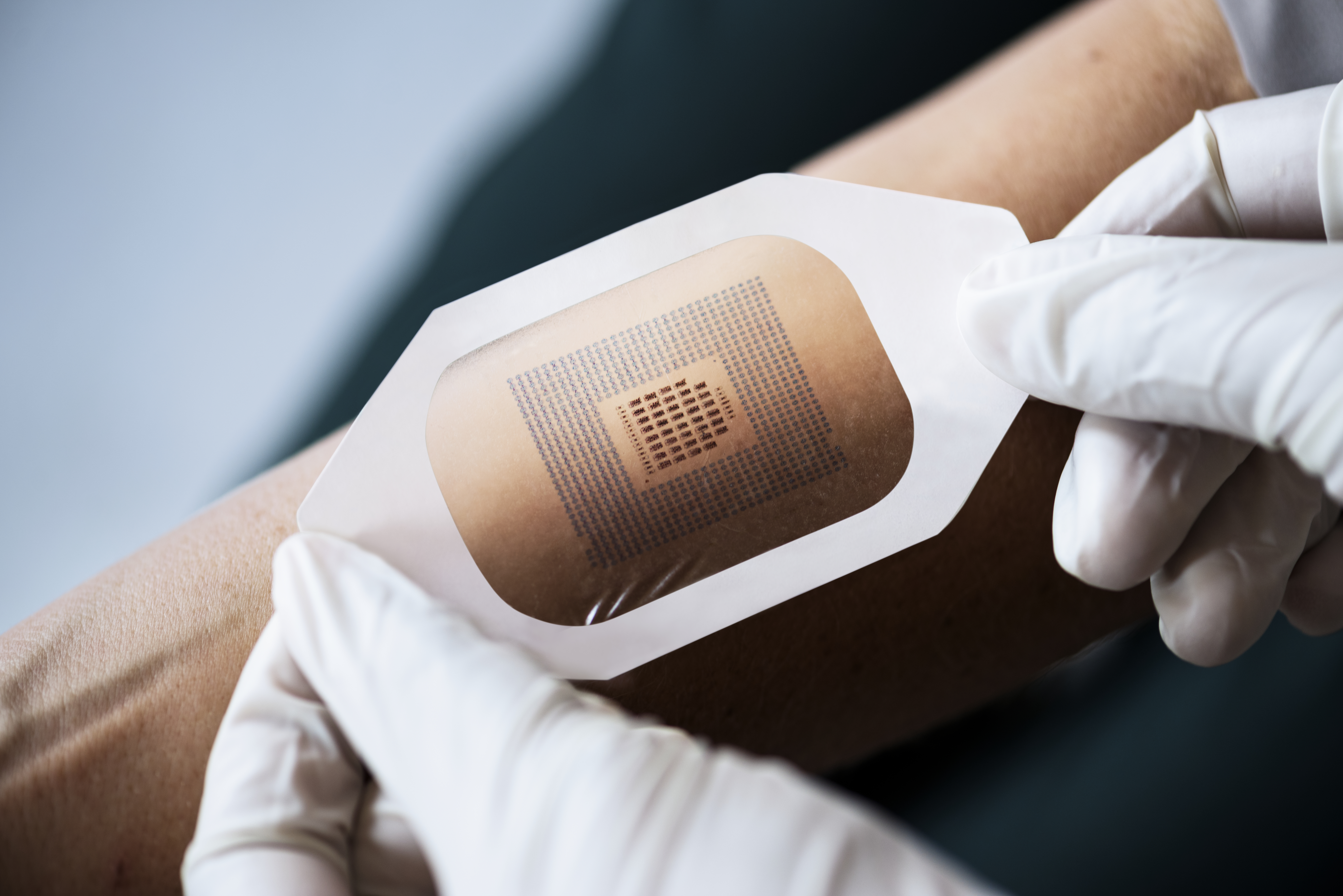
Medical electrodes create an interface between a patient and a machine, and are used to induce, measure or ground electrical energy. Types of medical electrodes include stress electrodes, monitoring electrodes, grounding pads and defibrillators.
This application requires a medical grade, skin friendly adhesive with conformable substrate to provide secure adhesion onto the skin, no adhesive residue after removal and compatibility with electrode hydrogel. To meet these needs, materials such as foams, films, non-wovens, microtapes or laminate backings can be used with low to high tack acrylics or rubber adhesives.
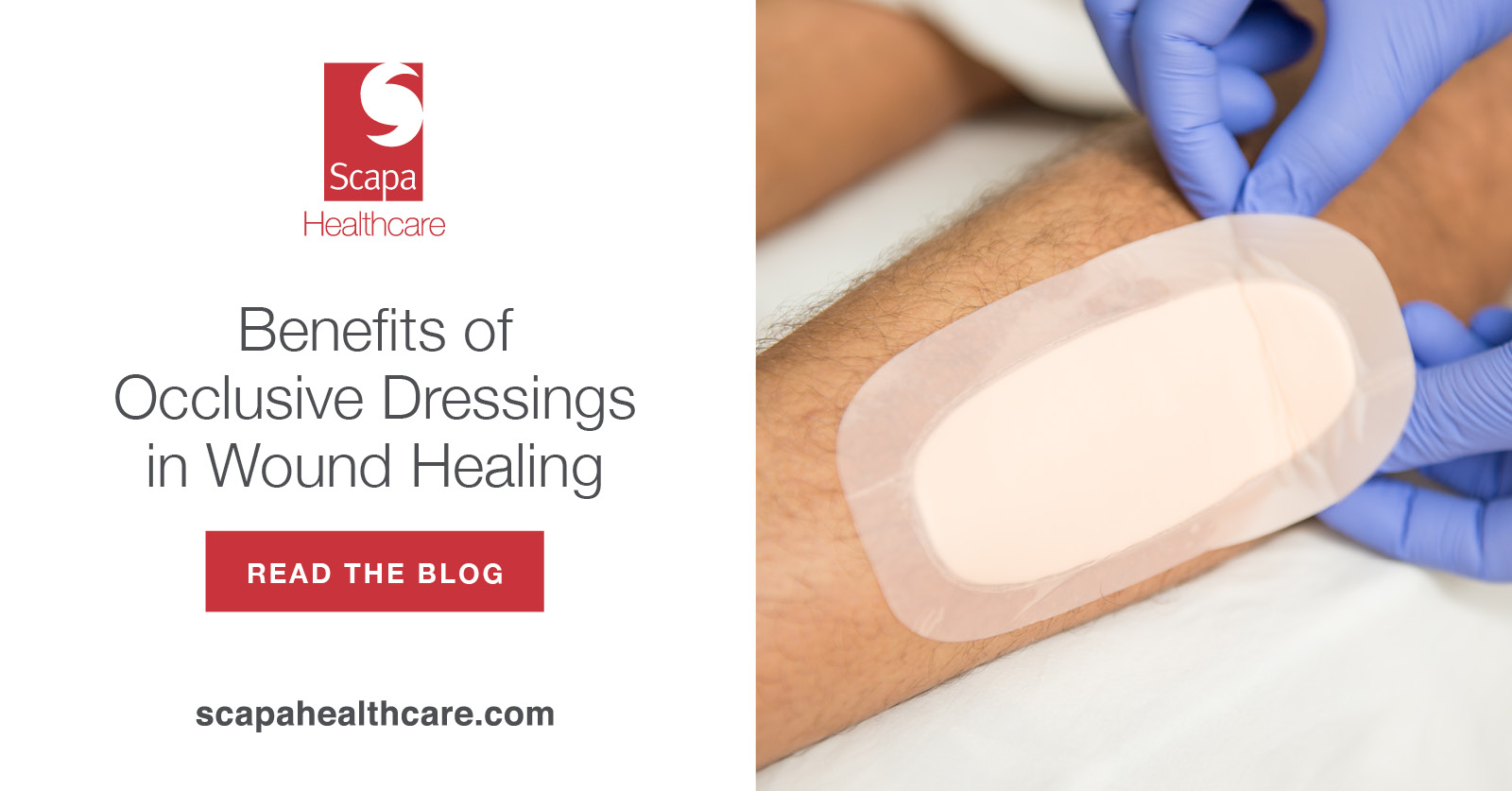
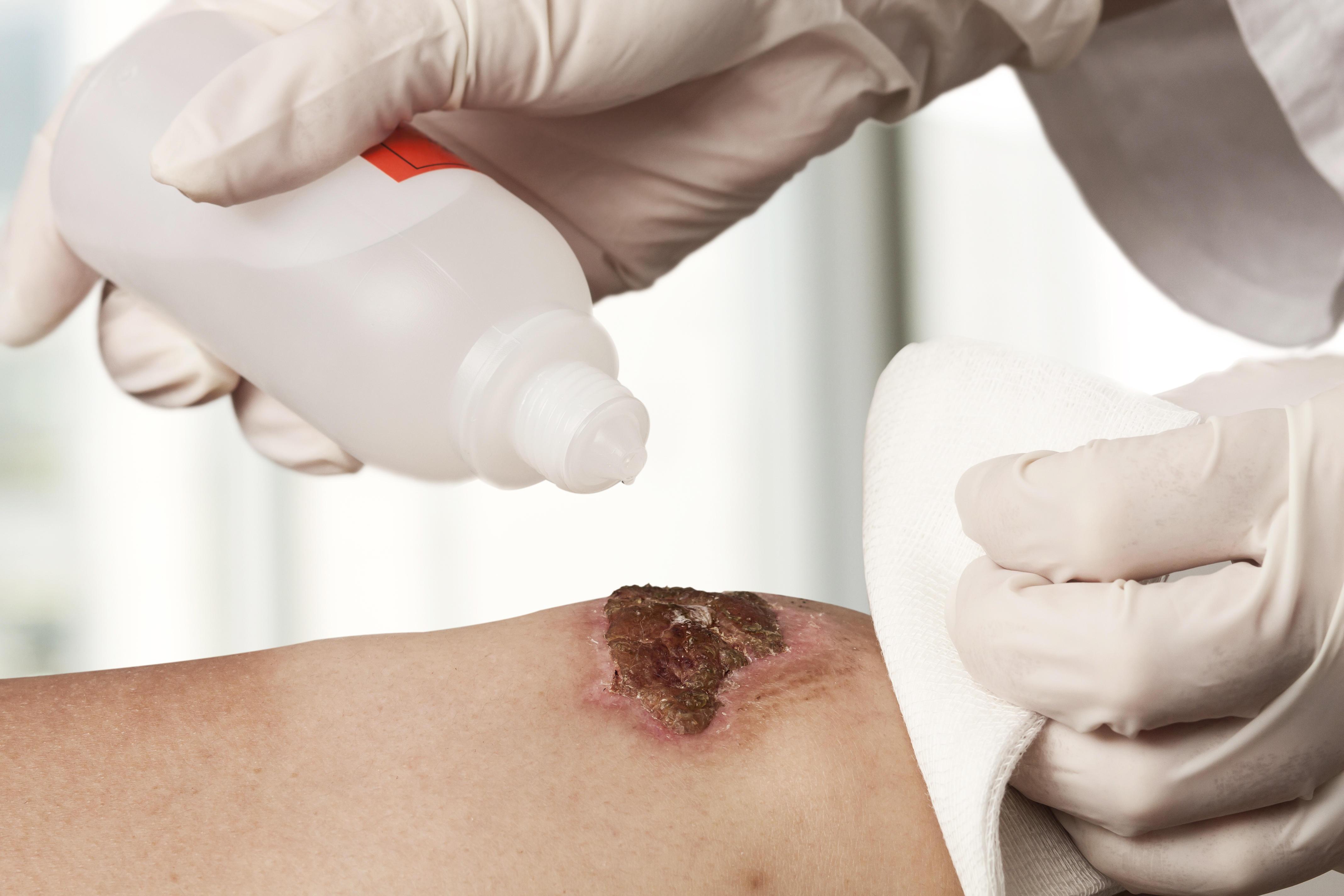
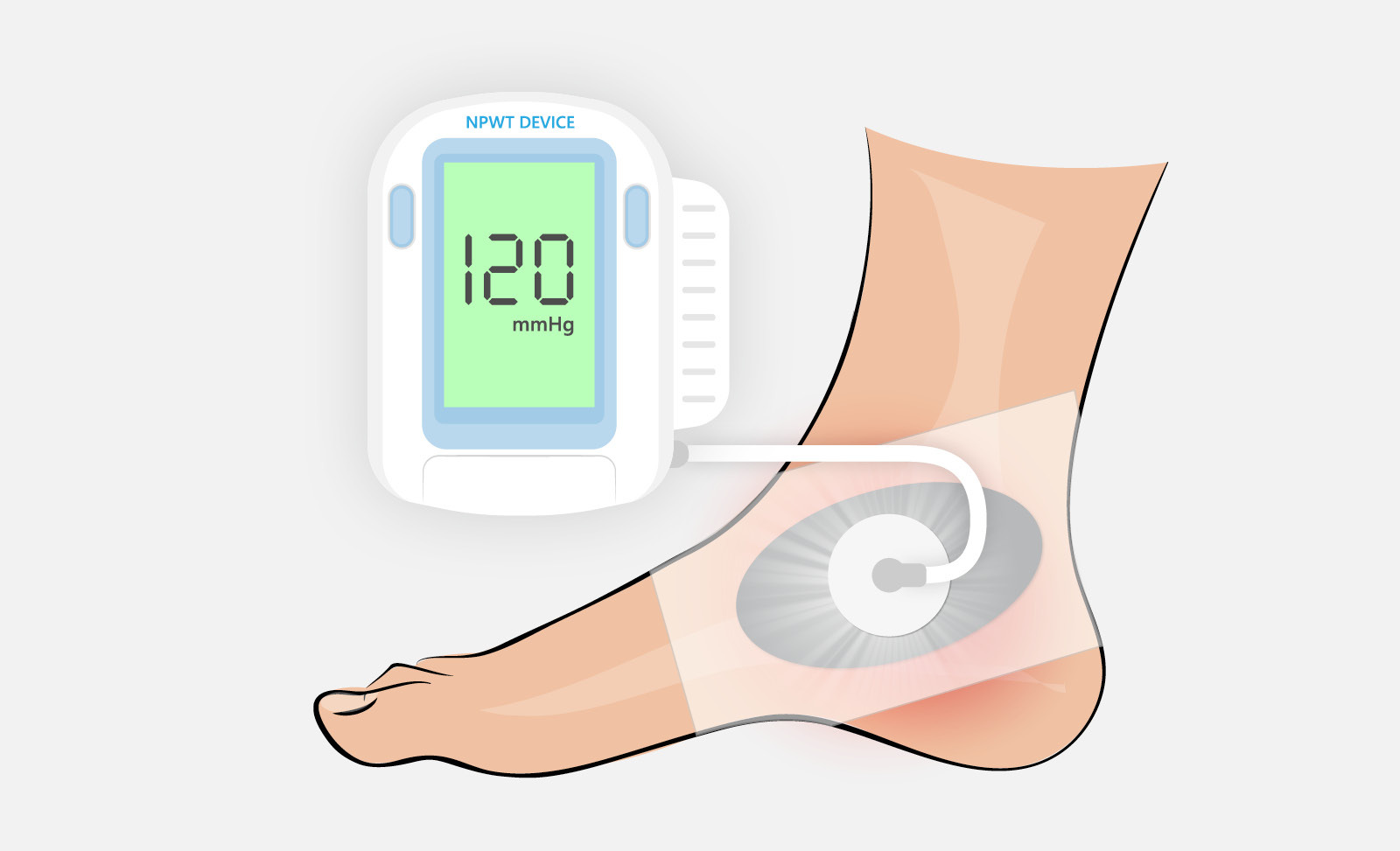
Advanced wound care dressings are used for hard to heal wounds and must offer a balance of exudate absorption and moisture retention in the wound bed. The most common advanced wound dressings include foams, hydrocolloids, alginates, hydrogels, silicone contact layers, transparent film dressings and negative pressure wound therapy drapes.
Requirements for professional wound care dressings include a medical grade, skin friendly adhesive, low to high breathable substrates and adhesives, a low coefficient of friction backing, secure adhesion to the skin, gentle and low skin trauma removal, discrete and conformable, and compatible to sterilization. To deliver on these needs, some of the medical adhesives used include acrylics, polyurethane (PU) gels, silicones, hydrocolloids and hydrogels on PU foams & films and non-woven backings. Advanced wound dressings could also include other materials such as alginates, collagens, super fibers and antimicrobial agents for specific applications.
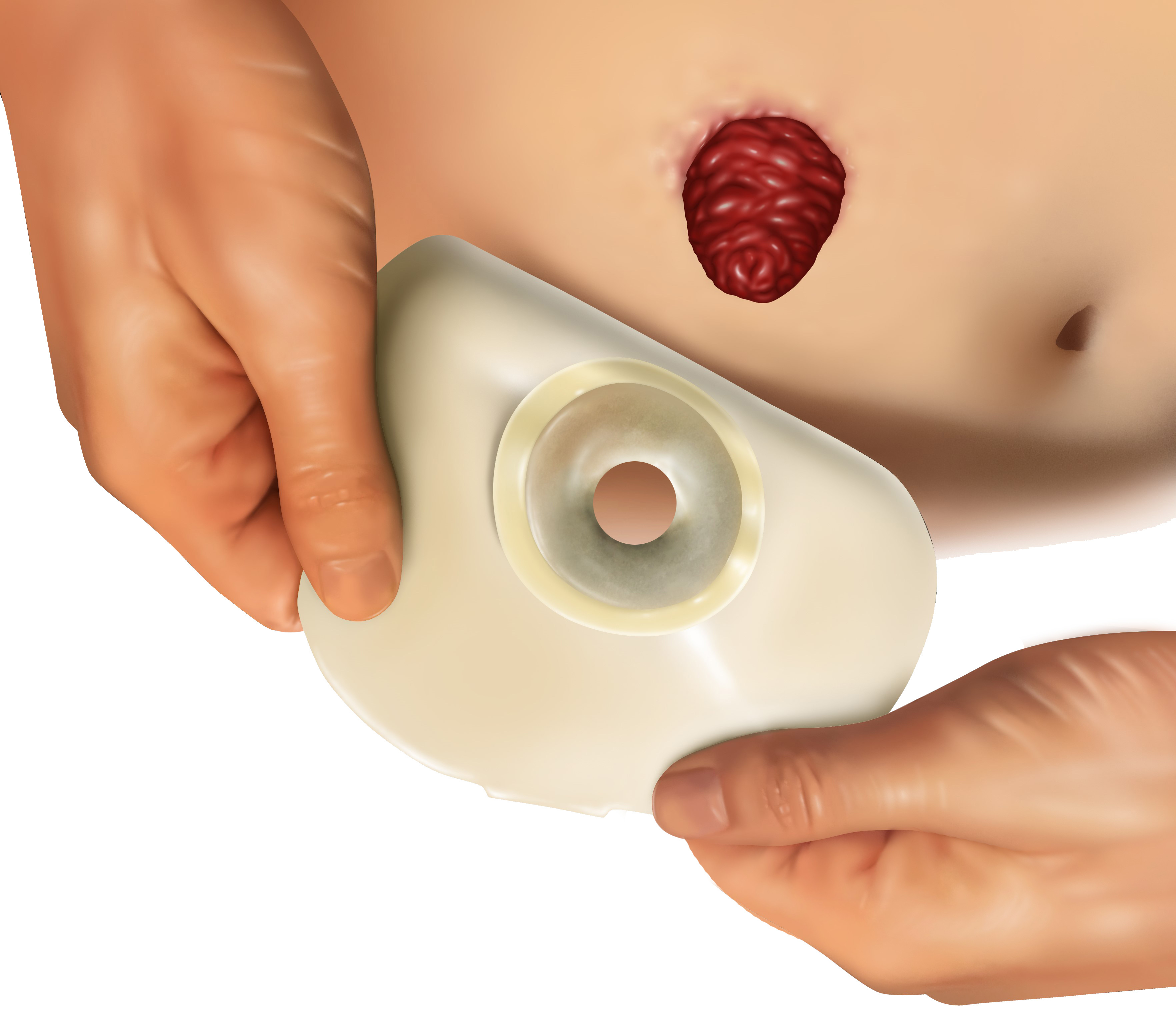
Ostomy bags are used to collect urine (urostomy), body waste (ileostomy), or stool (colostomy) when an opening has been created in the abdomen to by-pass a damaged part of the urinary tract or colon. Types of ostomy bags include one- or two-piece systems that are either closed, drainable or flushable.
This application requires medical grade, skin friendly adhesives and materials with high moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) that conforms to body contours and increase appliance wear time. For the ostomy bags, heat sealable backings for one-piece systems, high peel and shear adhesive for two-piece systems as well as water resistance and easy to clean materials are recommended. For the skin contact interface, some medical adhesives used include hydrocolloids, acrylics and silicones coated on non-wovens (polyethylene, polyester or ethyl-vinyl-acetate coated), polyethylene (PE) foams, or polyolefin or PU films backings.
Microplates are used for diagnostic tests such as DNA testing or infectious disease detection. The microplates must be sealed during testing or storage and adhesive materials are widely used for this purpose. Microplates are used in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Quantitative PCR (qPCR), immuno-assay, storage and transport, and cell culture applications.
Adhesive materials for microplates require optical clarity for fluorescence applications, light occlusion for light sensitive applications, gas permeability for cell culture, effective sealing to prevent evaporation and to avoid well to well contamination, no adhesive residue left on the plate, pierceable to recover samples, solvent resistance, and temperature resistance from -40 to +220 degrees Celsius. Typical adhesive materials include acrylics and silicones coated on polyolefin or polyester films, aluminum foils, and gas permeable substrate backings.
Surgical and Incise drapes protect the patient from bodily fluids during surgery. Incise drapes are used to create a sterile field and avoid microbial transfer from the skin to a surgical site. As a result, surgical drapes need an adhesive to bond well to non-wovens or films, and to skin, and provide resistance to body fluids. Incise drapes need high MVTR for long procedures as well as a transparent, nonreflecting film that is conformable. Typical adhesive materials used for surgical drapes include double-sided polyester tapes, acrylics and/or rubber adhesives. For Incise drapes, acrylic adhesives coated on a PU film with PE carrier are commonly used.
IV site dressings keep an IV system or catheter in place and protect the site from the external environment. Key requirements for this application include high MVTR to avoid moisture accumulation, transparency around the IV site to allow visual inspection, secure adhesion onto the skin & tubing and low trauma removal. Most IV dressings consist of acrylic adhesive coated on a high MVTR PU film with paper carriers or a non-woven (for reinforcement of dressing or strips to secure tubing).
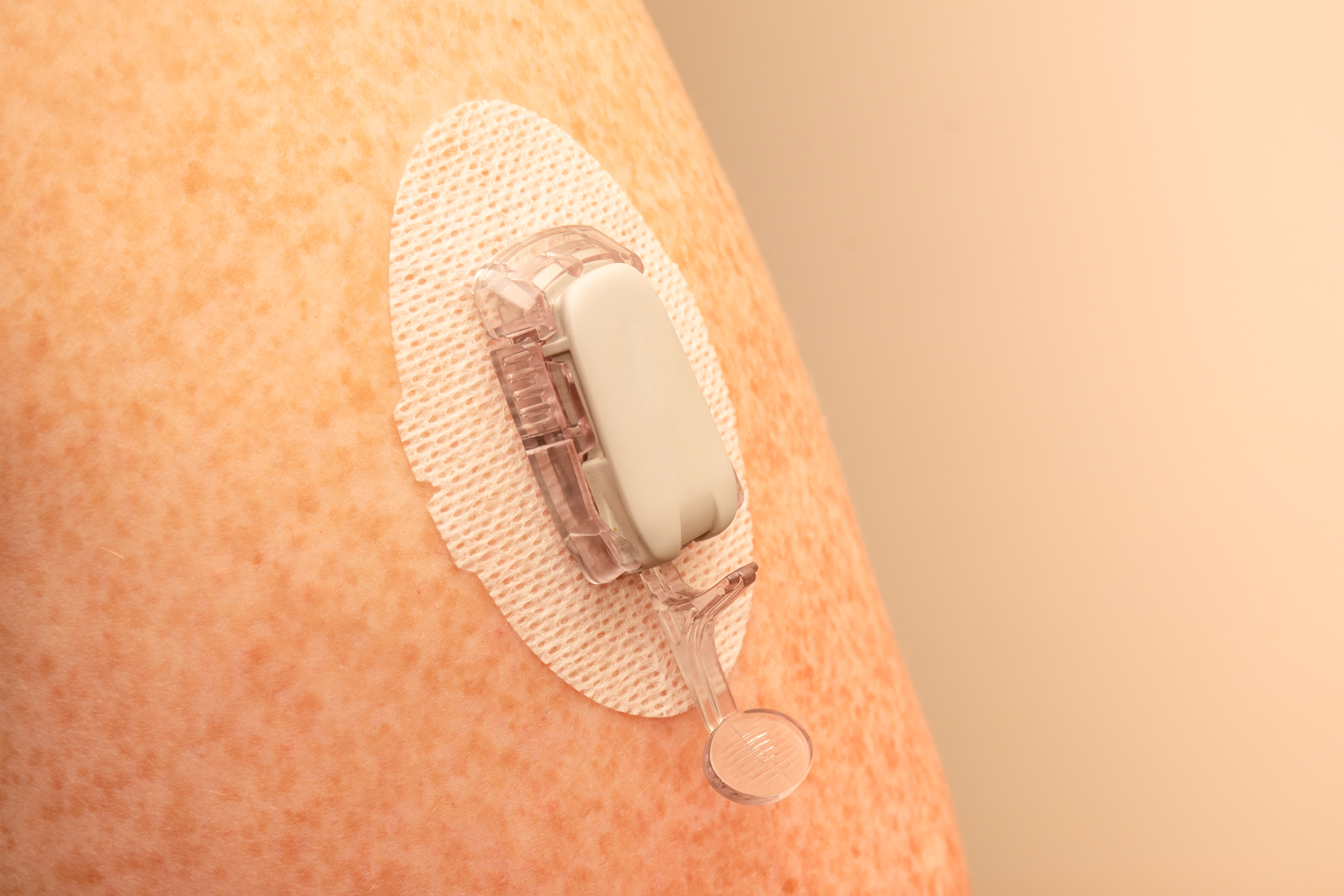
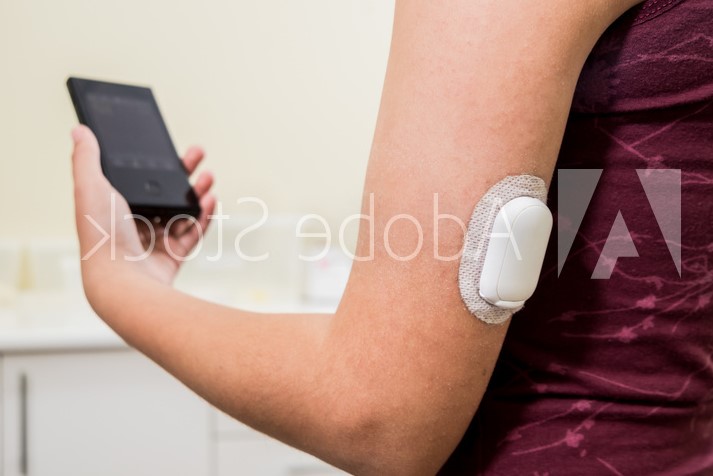
Diabetes care devices are designed to continuously monitor glucose levels as well as constantly deliver small quantities of insulin in the treatment of Type I & II diabetes. Fixation materials for this application must feature secure adhesion onto the skin for long periods of times (three to 14 days), and be breathable and conformable, with a backing weldable to plastic housing. To accomplish this, material constructions such as non-woven fabrics and PU films & foams coated with acrylic adhesives are commonly used.
How Scapa Healthcare Can Support Your Medical-Grade Adhesive Development NeedsSelecting the right adhesive, backing substrate and coating technique is critical in the development of medical fixation materials, as these elements can seriously affect performance, durability and comfort. Scapa Healthcare is a trusted, strategic partner of choice for contract manufacturing in the development of custom medical-grade adhesive solutions. Our team of experts and innovative technologies have helped many of the world’s leading companies in advanced wound care, consumer wellness, and medical device and fixation with their unique product development needs, from concept to development to full-scale production. Learn more about our medical adhesives and advanced materials portfolios.
View website